Concrete Testing Details
For Fresh Concrete:
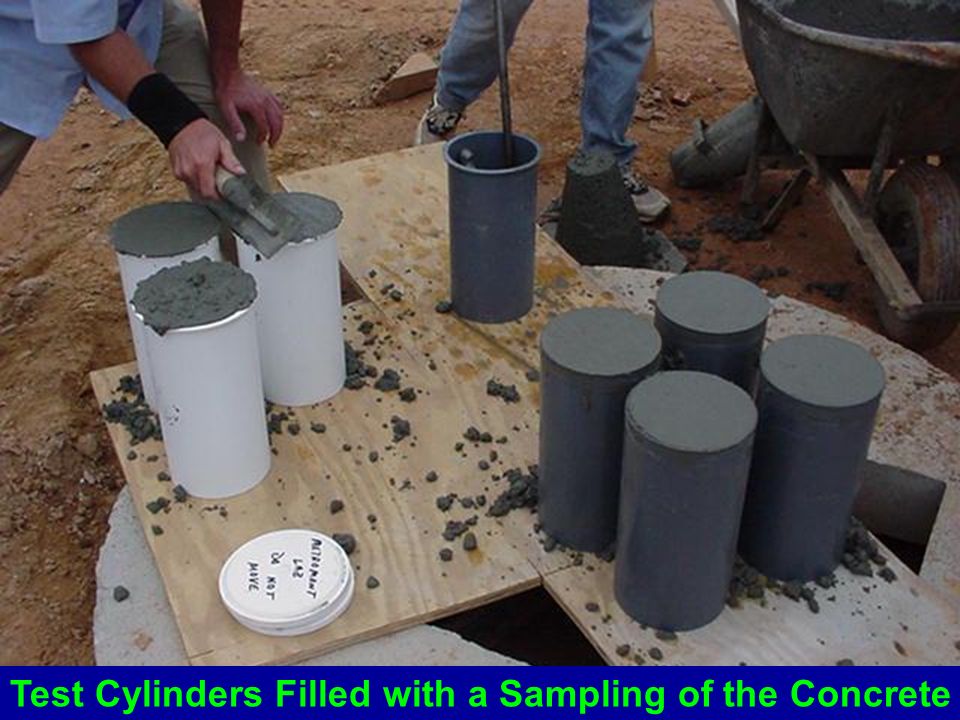
- Sampling fresh concrete
To ensure it is representative of the whole truck load, a standard sample consists of scoopfuls taken from different parts of the batch and collected in bucket.
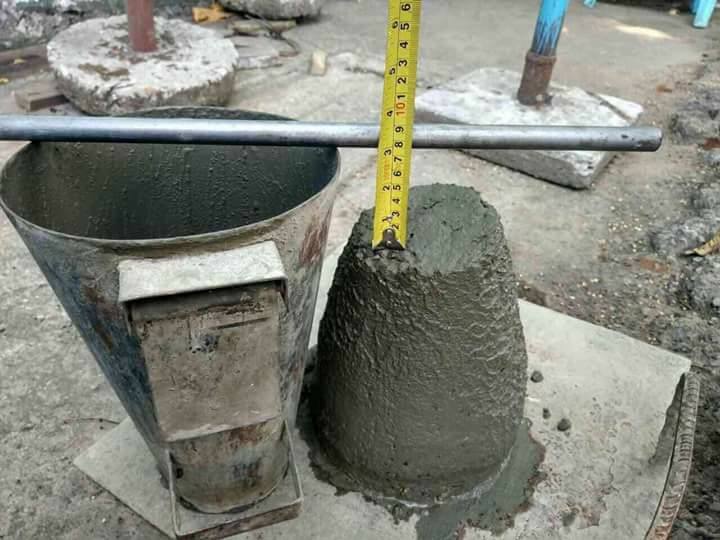
- Slump Testing
The slump Test of concrete is a principle of gravity flow of surface of the concrete cone that made in site and indicates the amount of water added to it, which shows the information on the workability and quality of concrete.
Test Method: PS-55-2-2015
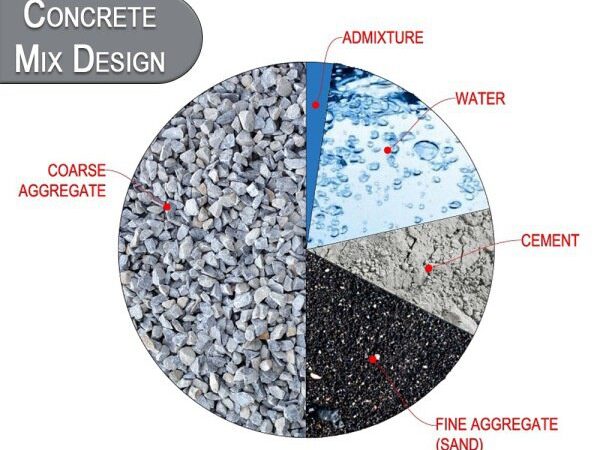
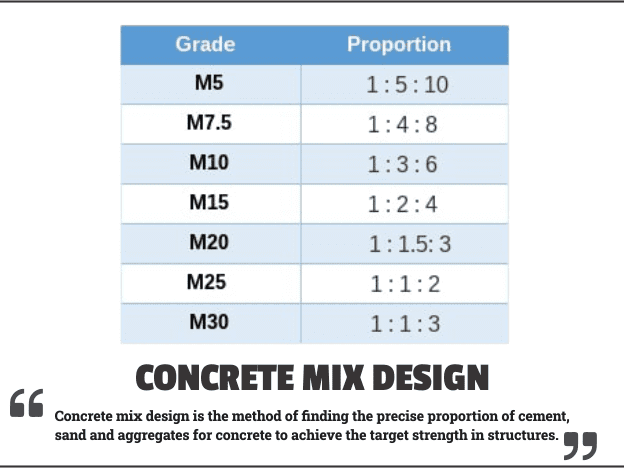
- Concrete Mix Design
This test helps in determining the suitable ingredients of concrete and determining their relative amounts with the objective of producing a concrete of the required strength, durability, and workability as economical as possible is termed as concrete mix design. It involves studying properties of Aggregate, Cement, Water & Admixture (if any), and is used to determine the proper Concrete Mix Design.




For Hardened Concrete:
- Compressive strength for obtaining specimens from field at 7 and 28 days from casting.
The cube test is most commonly used for determining the value of compressive strength that can be used to assess whether the batch that the concrete cube represents, meets the required compressive strength or not. A cube of concrete in the cast is cured for the appropriate time and is then compressed between two parallel faces.
Test Method: PS-55-2018
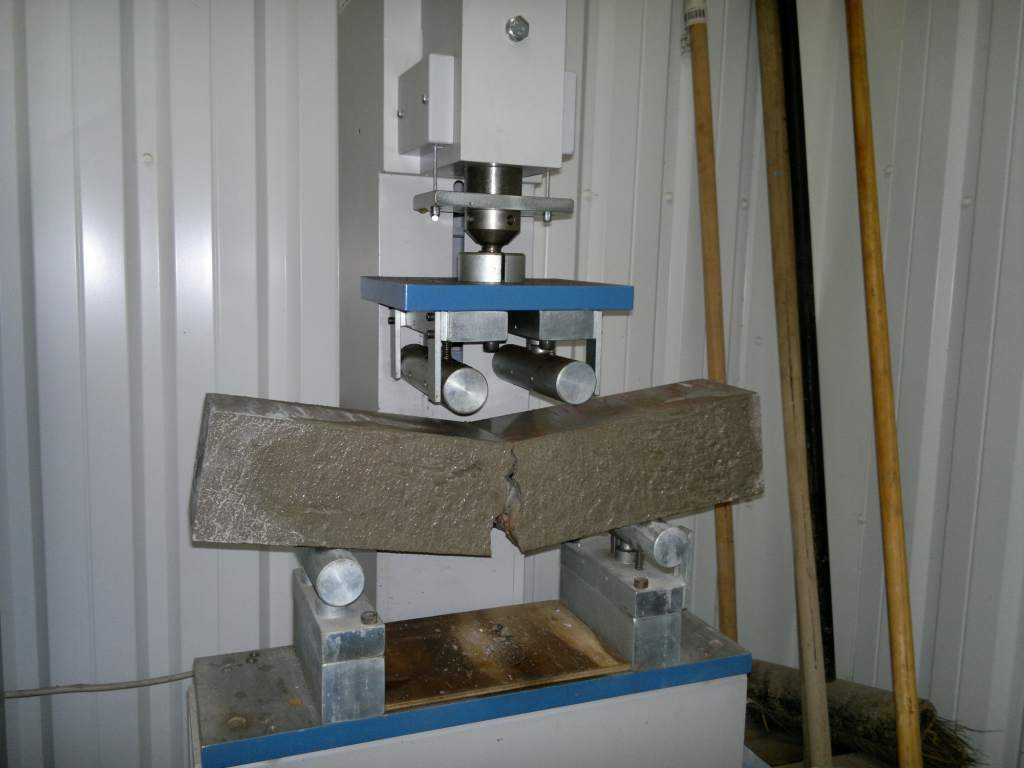
- Flexural strength for obtaining specimens.
Flexural Strength is the ability of a beam or slab to resist failure in bending. It is measured by loading un-reinforced concrete beams until failure.
Test Method: PS-55-4/2018
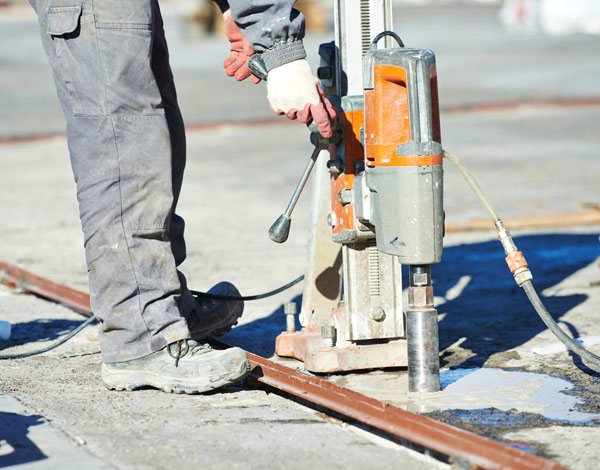
- Obtaining and testing Concrete Cores.
Core tests are generally performed to assess whether suspect concrete in a new structure complies with strength-based acceptance criteria or not. In addition, it is critically used to determine in-place concrete strengths in an existing structure for the evaluation of structural capacity.
Core tests are generally performed to assess whether suspect concrete in a new structure complies with strength-based acceptance criteria or not. In addition, it is critically used to determine in-place concrete strengths in an existing structure for the evaluation of structural capacity.
- Dimension Measurement
- Measurement of moisture content in the sample after its normal drying
- Density
- Absolute water absorption
This test helps in determining the rate of absorption of water in cement concrete by measuring the increase in the mass of a specimen resulting from absorption of water during the time when one surface of the specimen is exposed to water. The exposed surface of the specimen is immersed in water and water ingress of unsaturated concrete dominated by capillary suction during initial contact with water.
Test Method: PS-55-4/2018
- Capillary absorption
Capillary absorption represents the main mechanisms for water and water vapor transport in concrete. The capillary absorption of concrete increases with an increasing content of rubber particles due to its poor bonding with hydrated cement paste
Test Method: PS-55-4/2018
- Abrasion resistance
This test is determining the relative abrasion resistance of horizontal concrete surfaces. The procedures differ in the type and degree of abrasive force they impart, and are intended for use in determining variations in surface properties of concrete affected by mixture proportions, finishing, and surface treatment. They are not intended to provide a quantitative measurement of the length of service that may be expected from a specific surface.
Test Method: PS-55-4/2018
- Modulus of elasticity
- Cement content in Concrete
Testing of concrete for cement content is done by crushing a sample of the concrete obtained from the concrete through core sampling. The concrete is then crushed and the resulting fine powder tested chemically. This determines the insoluble residue, lime content, and soluble silica.
Test Method: PS-55-4/2018
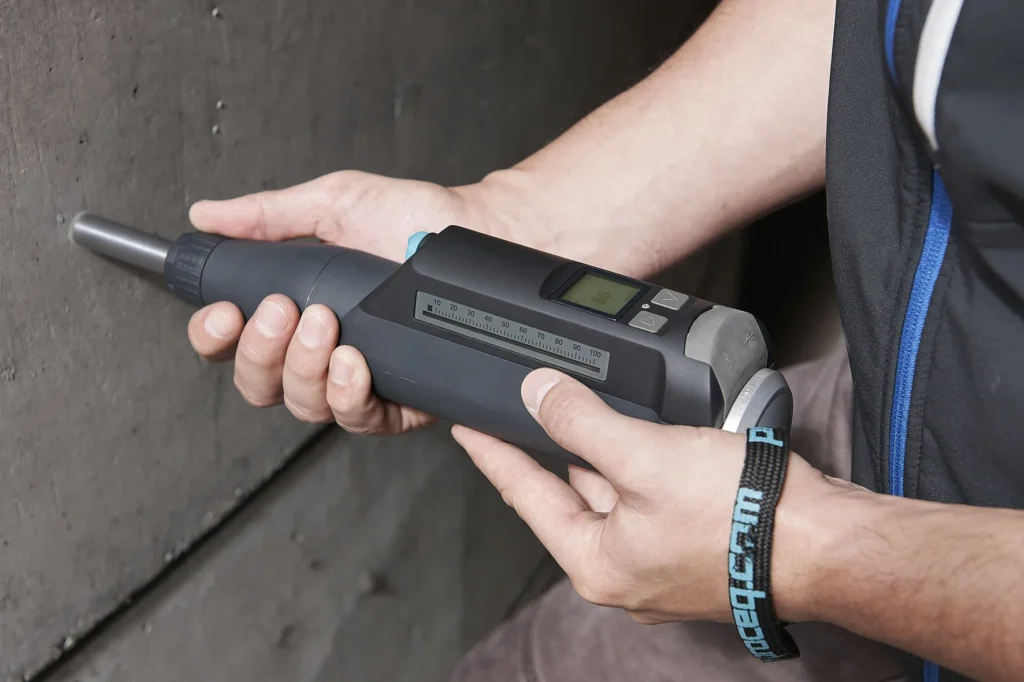
- Non-destructive Hammer Test
Rebound hammer test is a cost-effective, and rapid solutions for non-destructive evaluation of concrete strength. Our experienced engineers and technicians utilize the most advanced tools to assess Concrete uniformity and homogeneity over large areas, such as walls and slabs and In-place (on-site) Estimate of Concrete Strength in addition to Development of correlation curves between compressive strength, and rebound values.
- Non-destructive Ultrasonic testing
Ultrasonic concrete testing is based on the pulse velocity method to provide information on the uniformity of concrete, cavities, cracks and defects. The pulse velocity in a material is directly proportional to its density and its elastic properties which in turn depends on the compressive strength and the quality of the concrete. It is, therefore, feasible to obtain information about the properties of components by sonic investigations.
- Pile Integrity
This test is done to measure Pile length, depth to anomalies, Pile head stiffness, Pile shaft mobility – which is dependent on pile section and concrete properties.
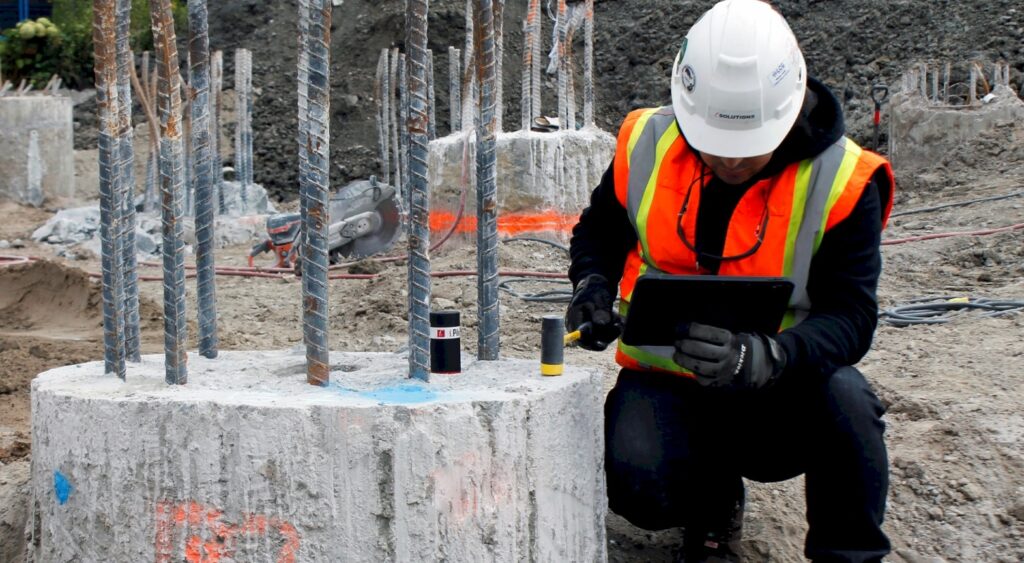
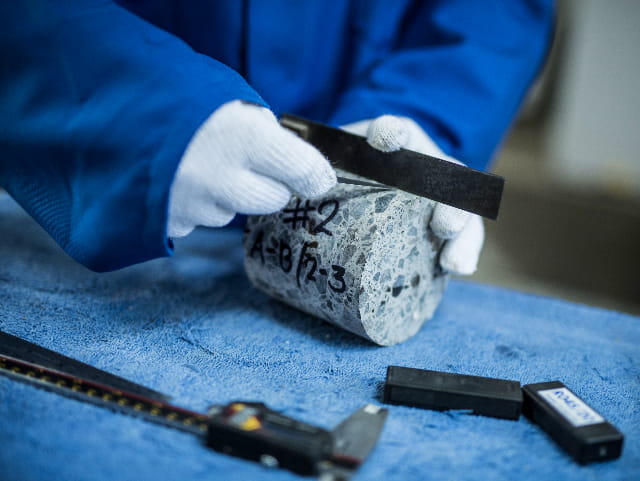
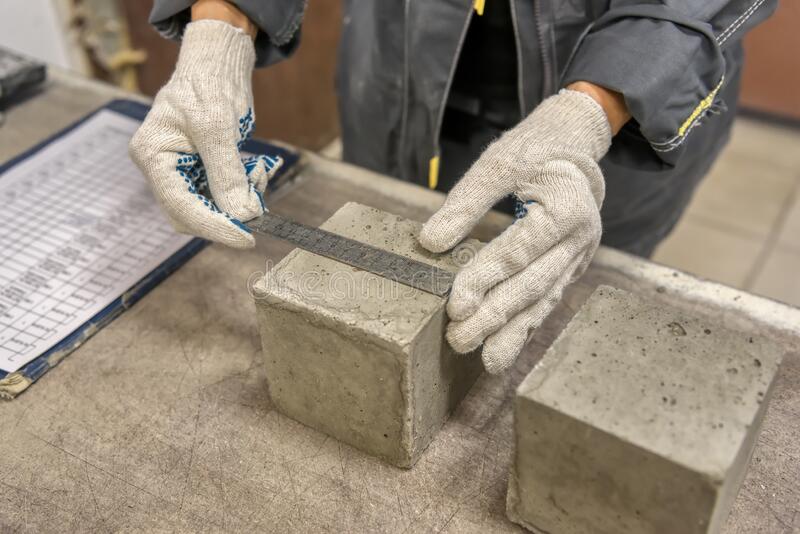










These are just a small selection of the Special Inspection services that our team offers. Contact our trusted team of engineering today to learn more about our full suite of services and Special Inspections.